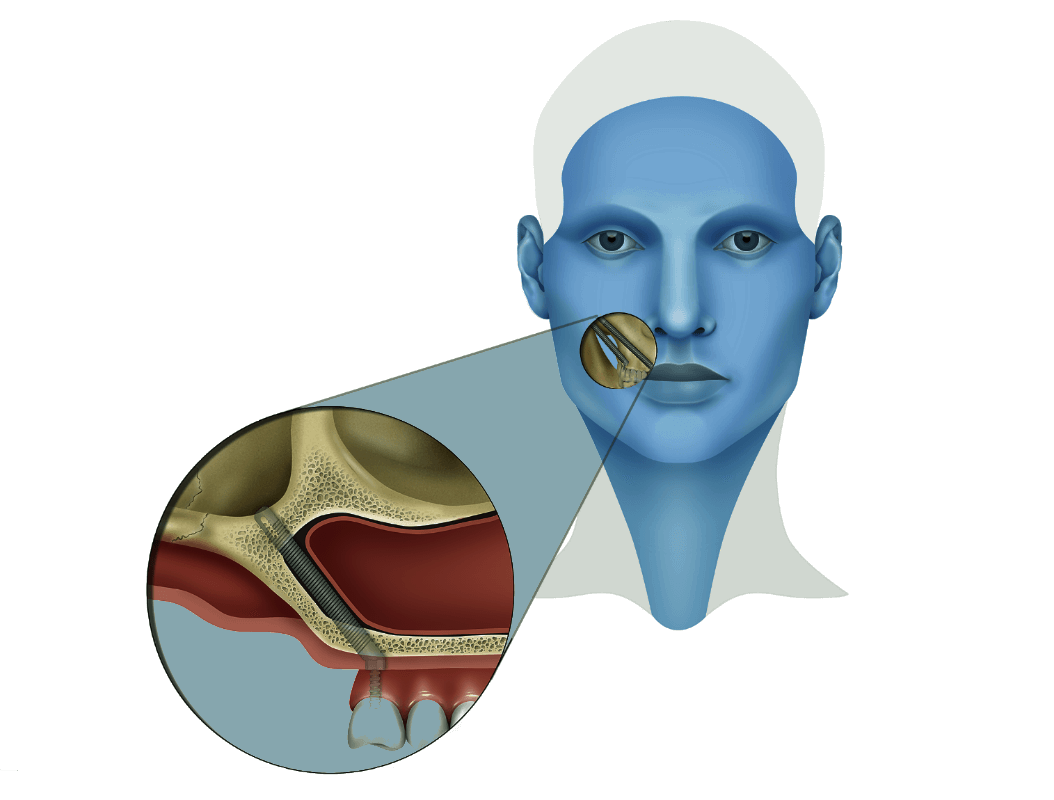
Pterygoid Implant
Pterygoid that is located in the region of the sphenoid bone, implant insertion is an alternative method to avoid sinus-lifting or other grafting procedures to treat the posterior maxilla. These type of implants are especially used in partial toothlessness in order to avoid distal cantilevers. The placement of this implant requires surgical experience.
The cumulative survival rate over a 10 year period for Dental Implants placed in this particular region is reported to be 91%. The main reason for using pterygoid implants is the availability of dense cortical bone of the pyramidal process and the plate lying in the region of the inferior part of the sphenoid bone of the vertebrate skull.
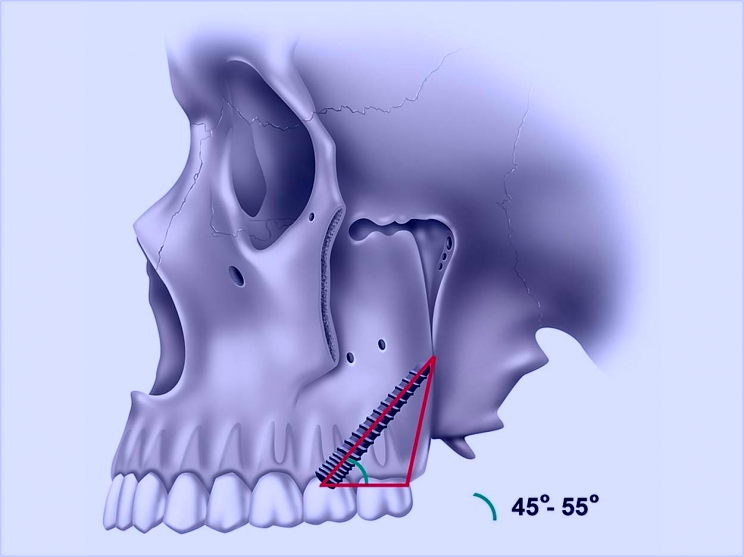
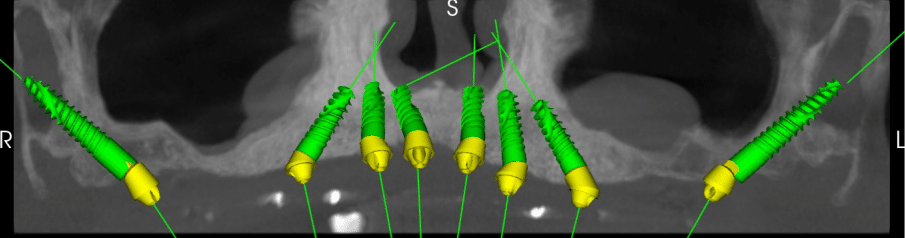
Characteristics Of Zygomatic And Pterygoid Implants
The main characteristic of these implants is that they are placed in two bones that are never reabsorbed, the zygomatic, in the case of zygomatic implants and the pterygoid, in the case of pterygoid implants. So they can be used even in the most severe atrophies of the maxillary bone. In addition, zygomatic and petrigoid implants are also special for their length, much longer than conventional implants. Thus, zygomatics have a length of 30 to 55 mm and pterygoids of 15 to 20 mm, a length designed to ensure a correct anchorage in the bone.
Treatment with zygomatic or pterygoid implants has three major advantages:
- It is a good alternative to bone grafts placement fin patients suffering considerable maxillary bone resorption.
- Shortens the treatment time safely, quickly and conveniently for the patient.
- It guarantees improved aesthetics for every patient, regardless of the quality of their bone for dental implant placement. However, zygomatic and pterygoid implant placement is sometimes accompanied by the use of normal implants, depending on the quality and quantity of the patient’s bone.